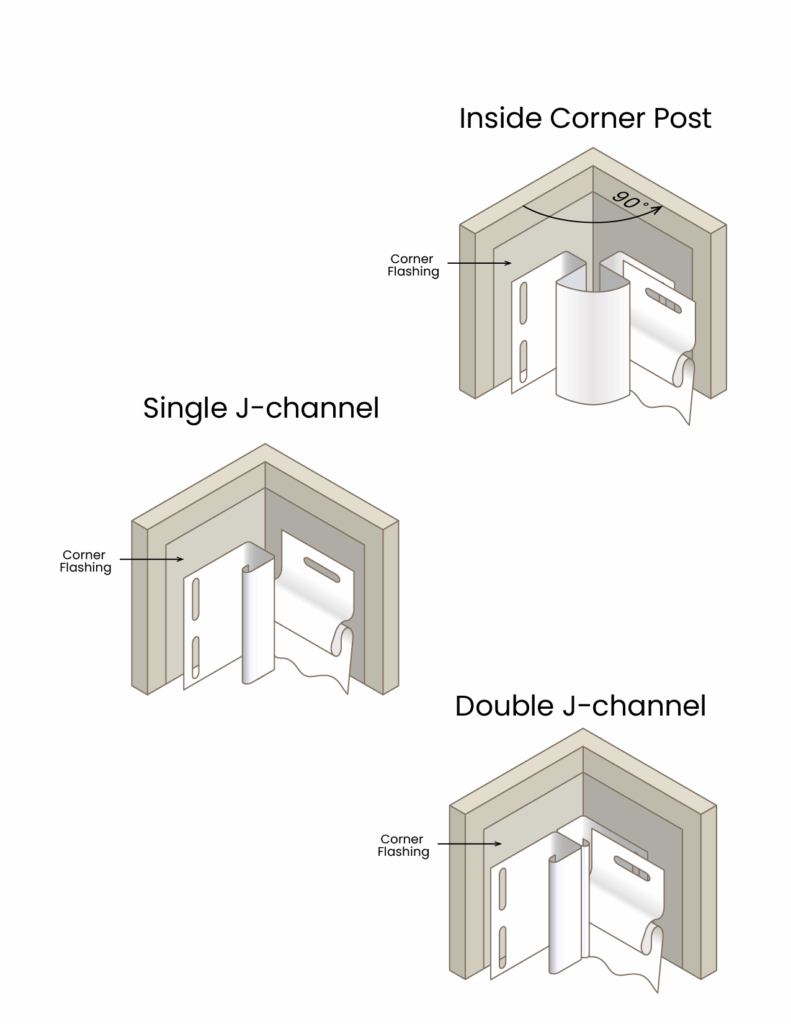
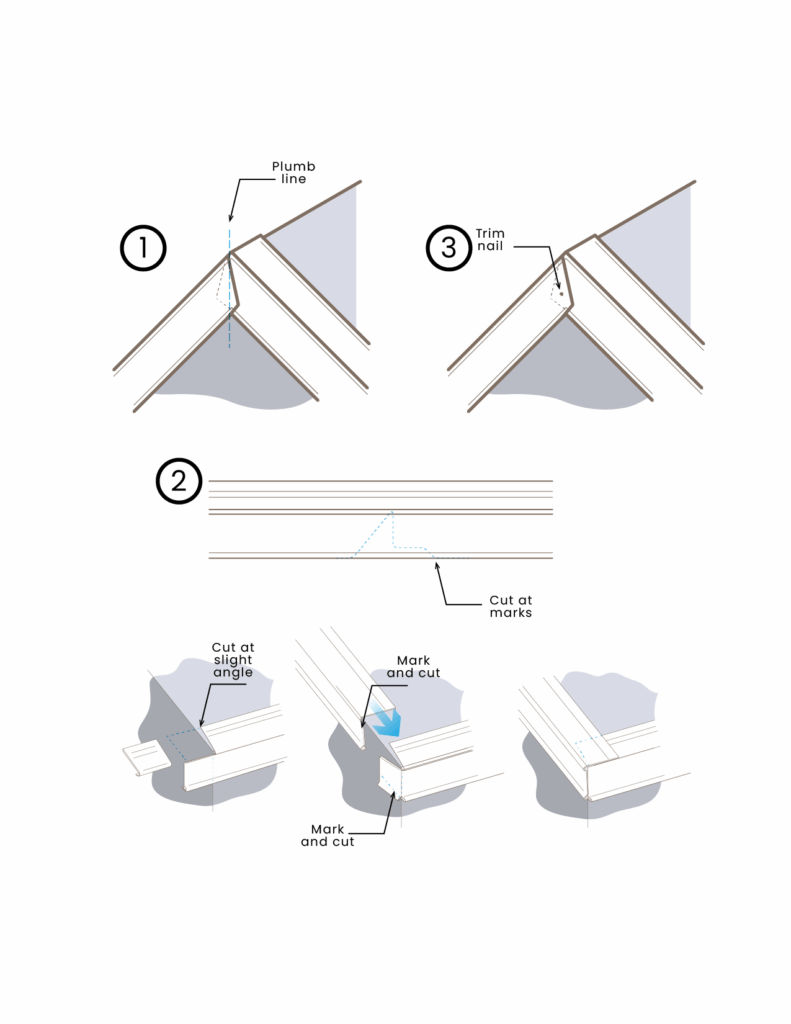
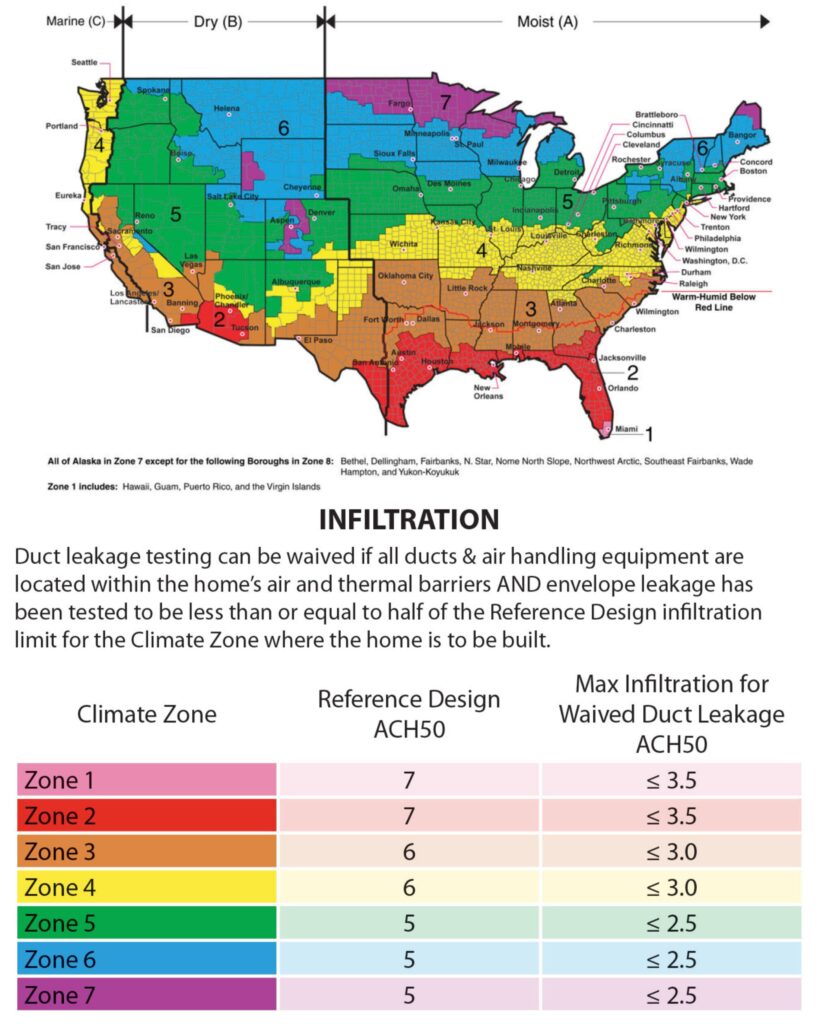
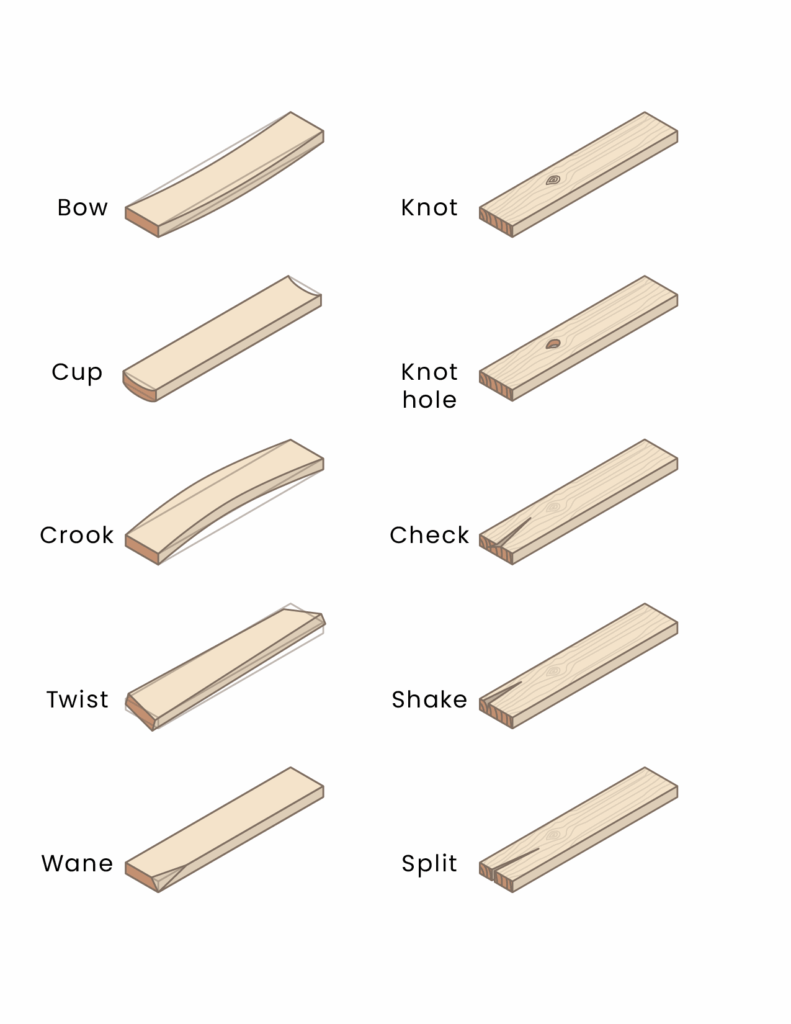
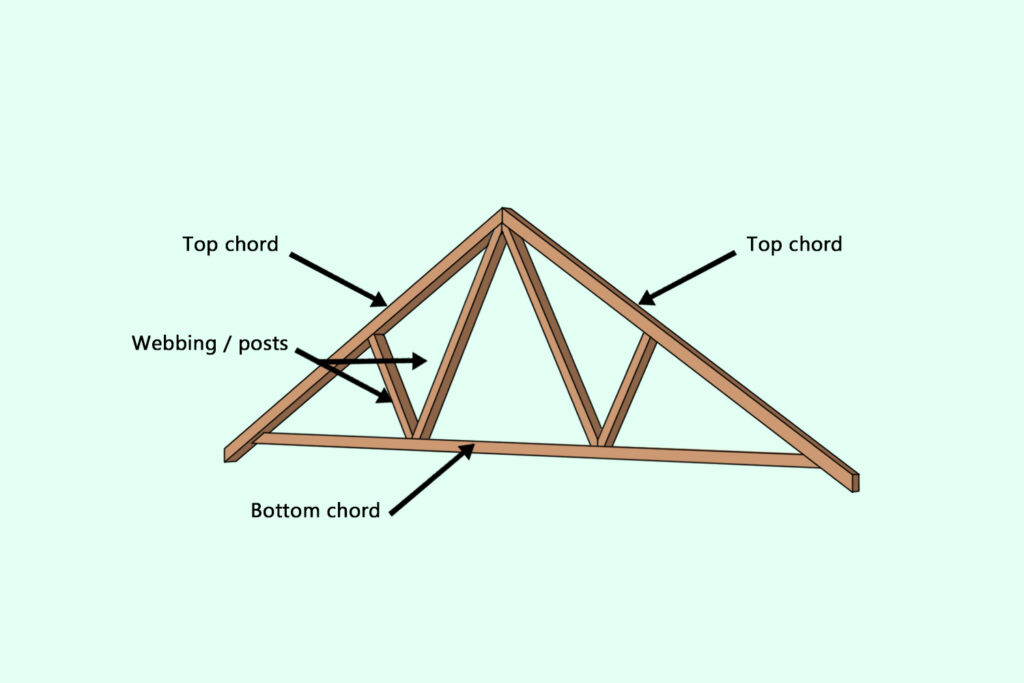
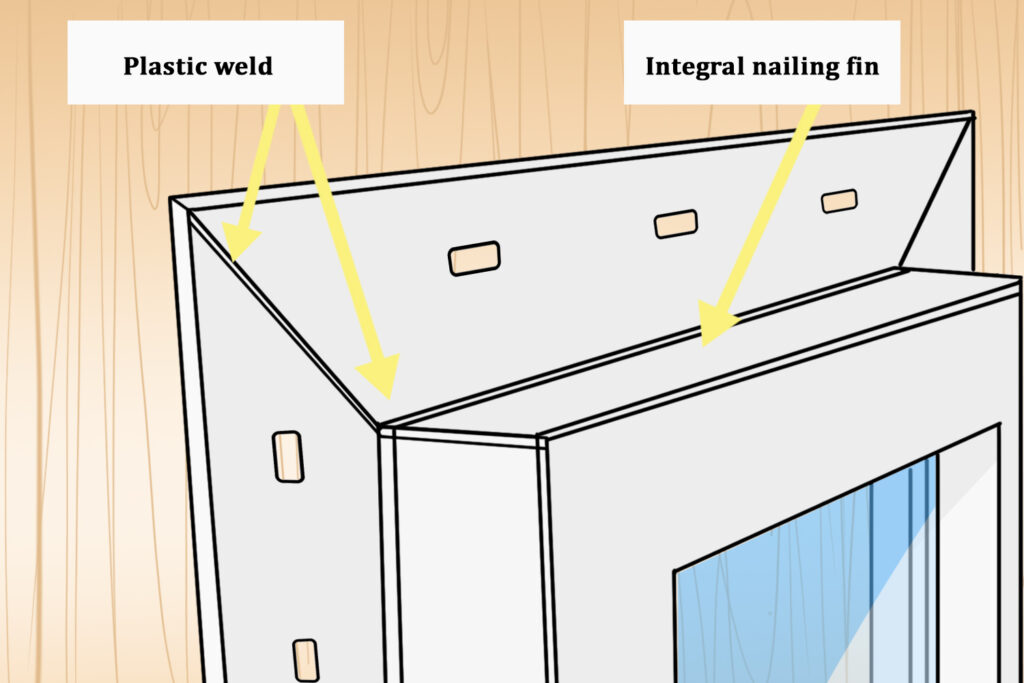
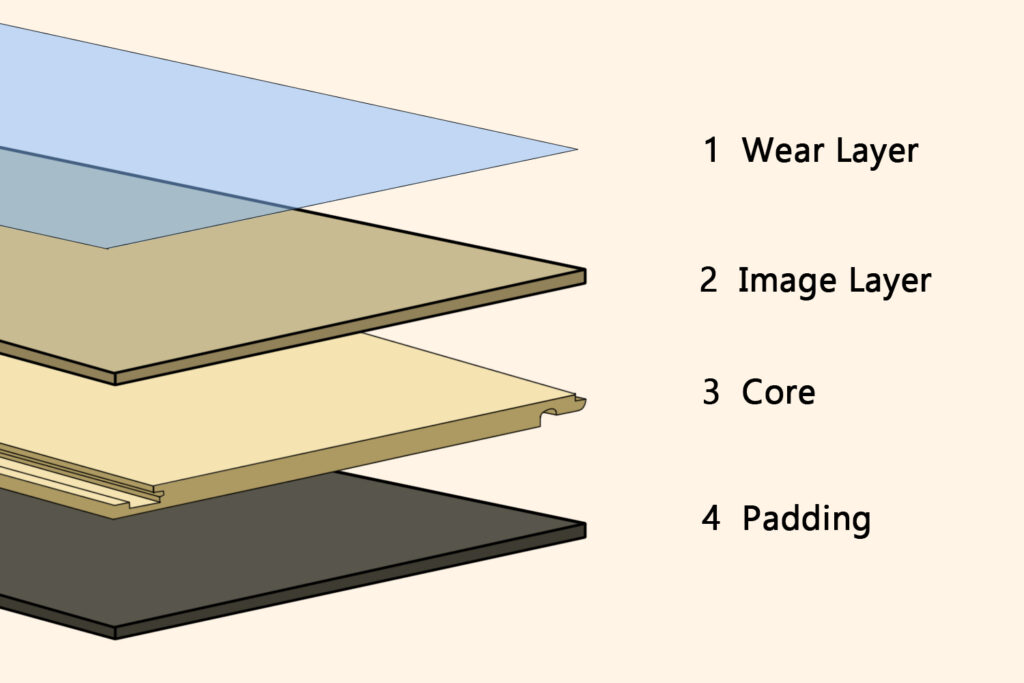
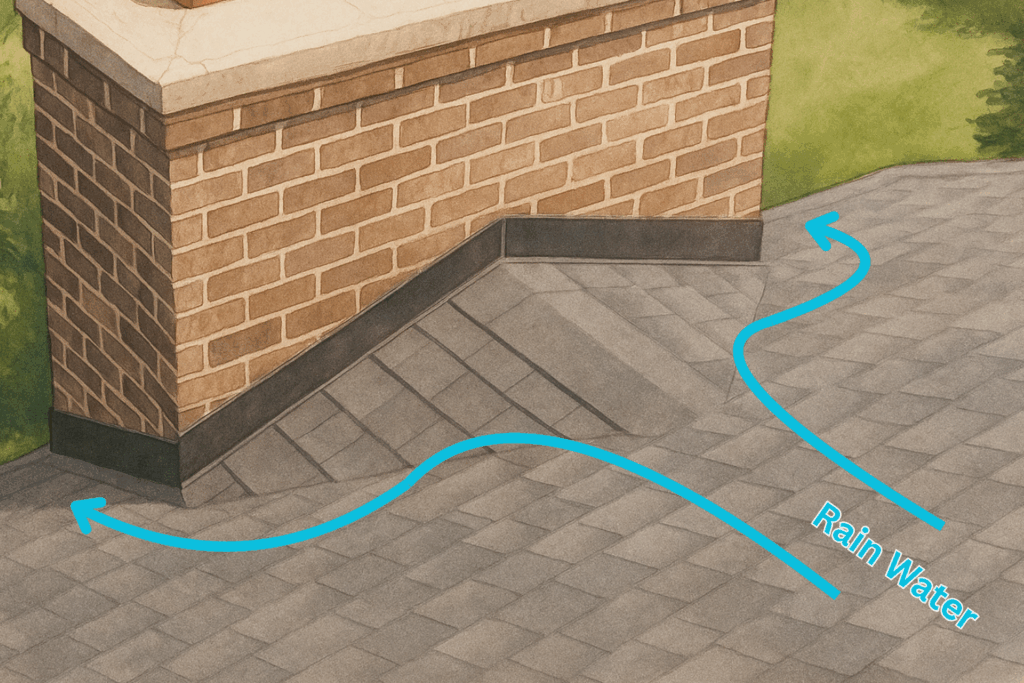
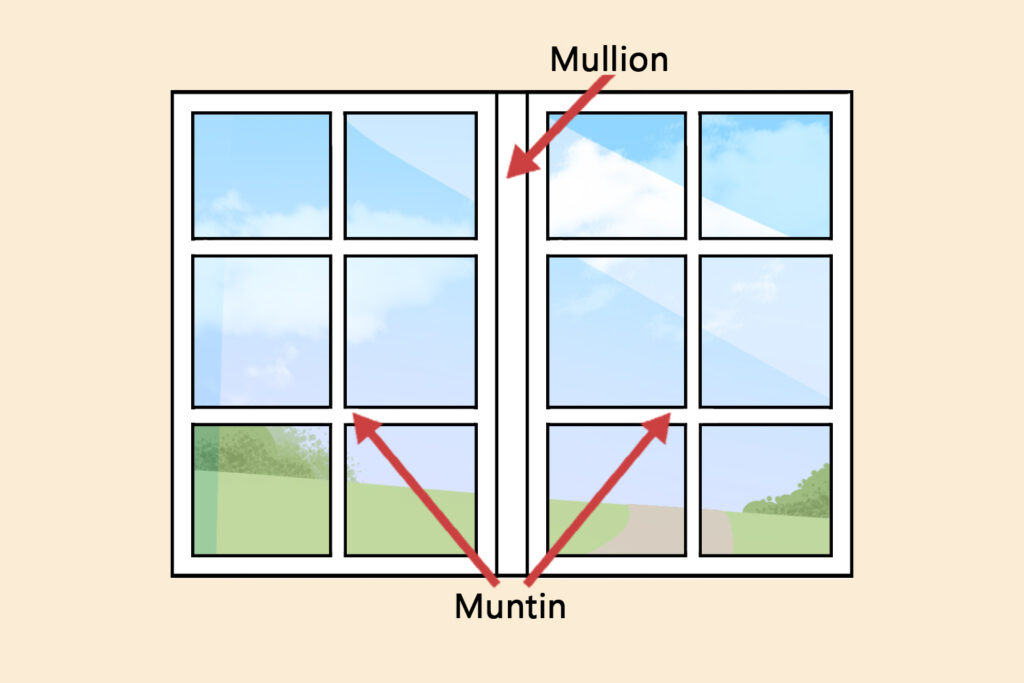
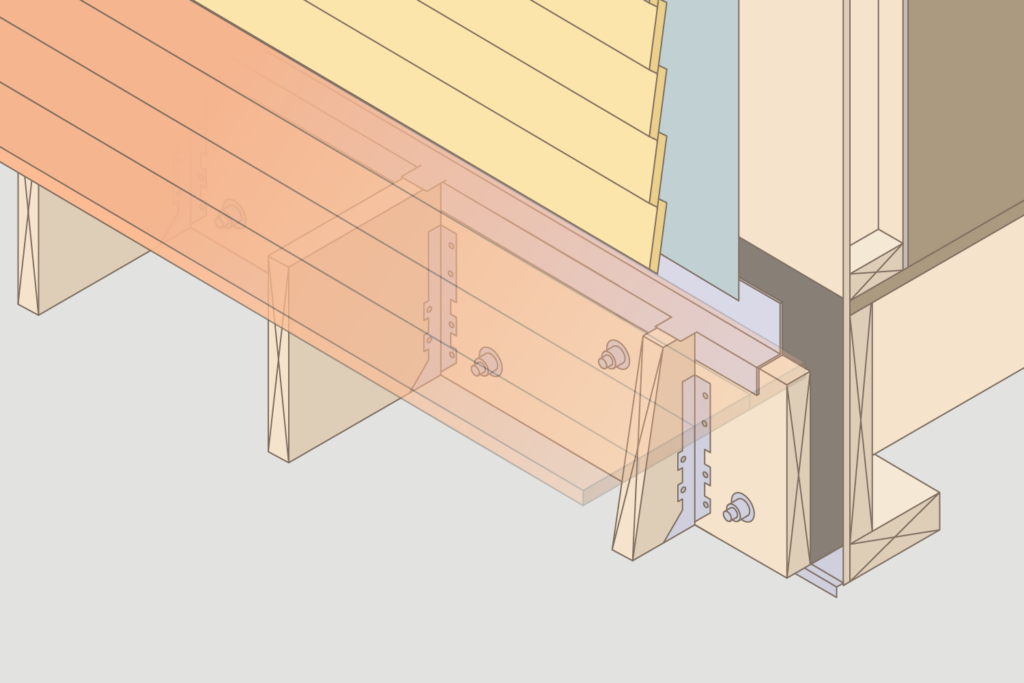
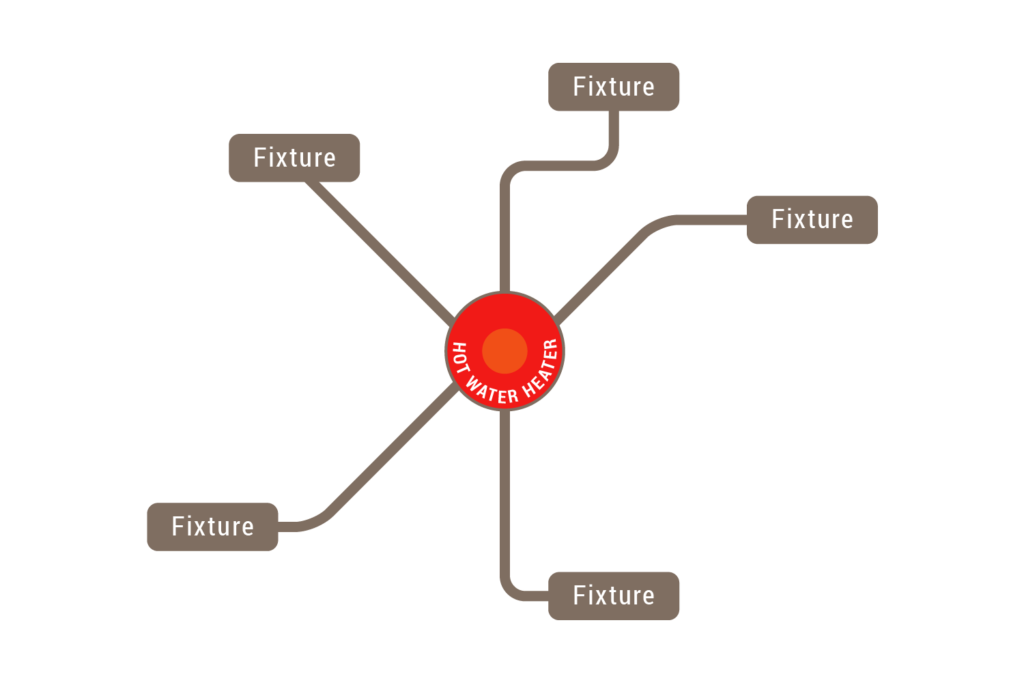
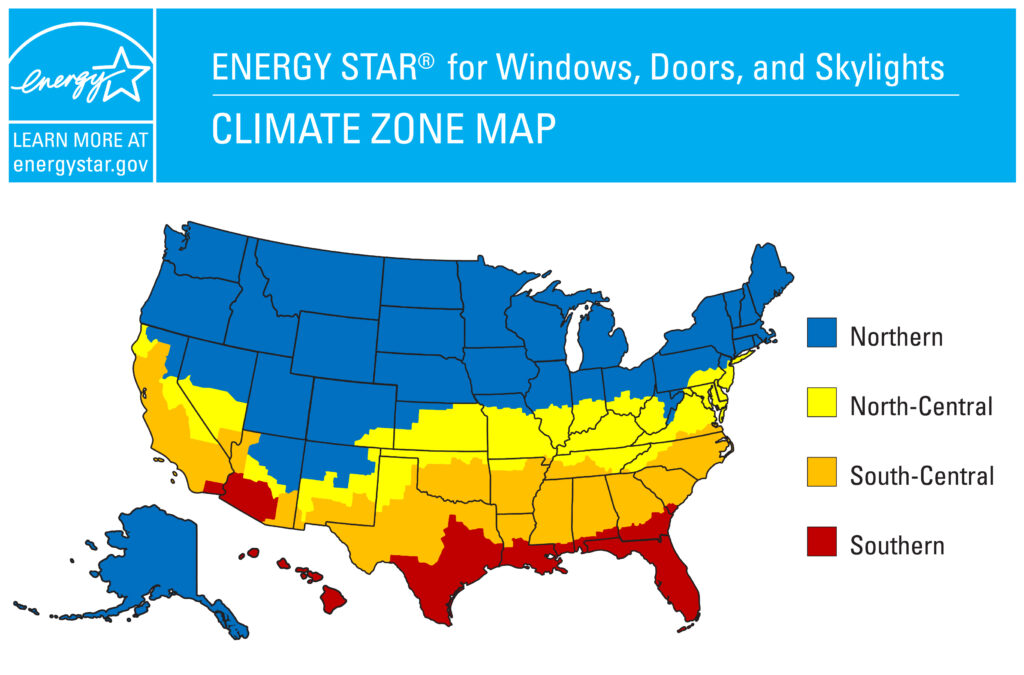
Both are common types of concrete floors systems used in construction, but they have different characteristics and applications.
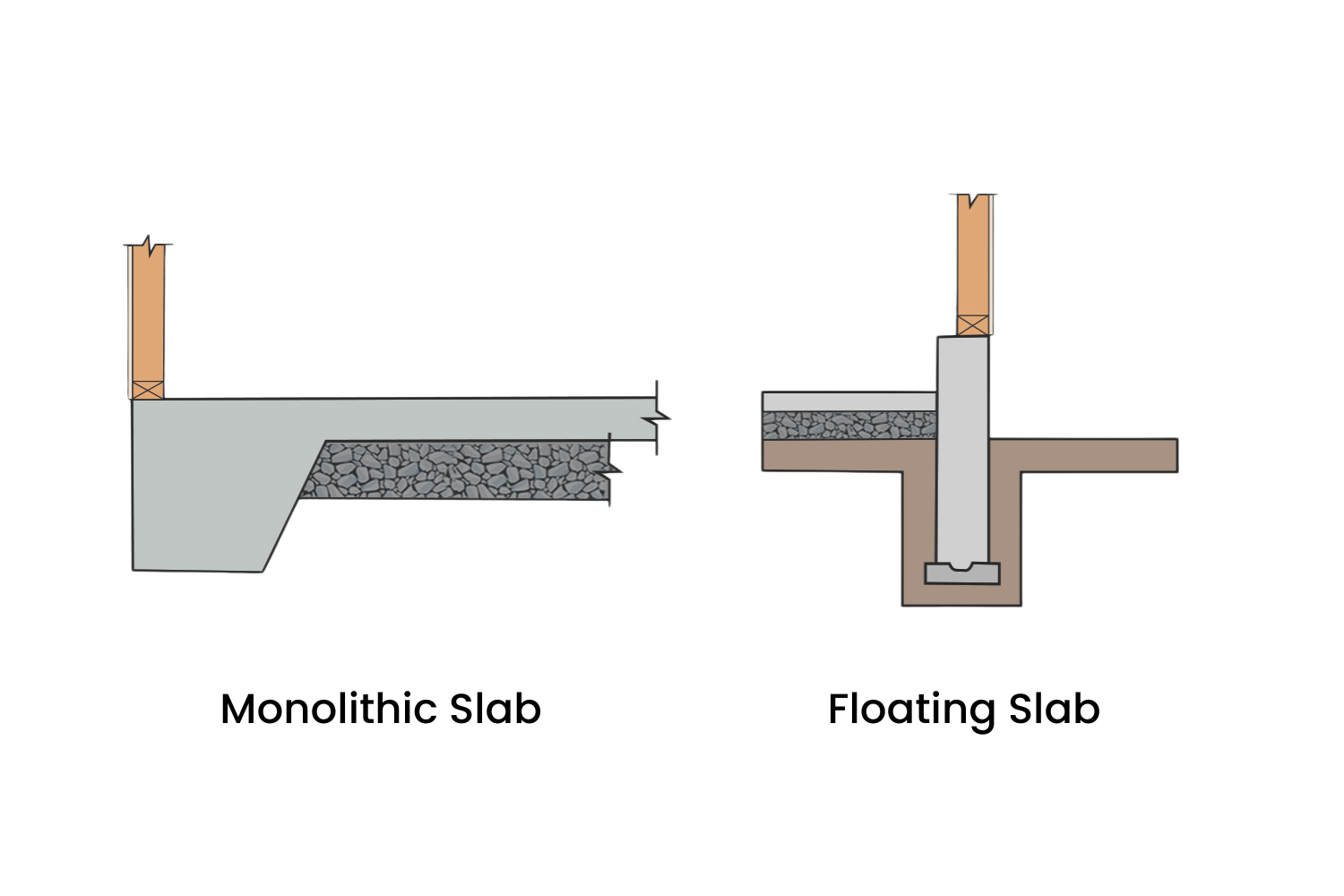
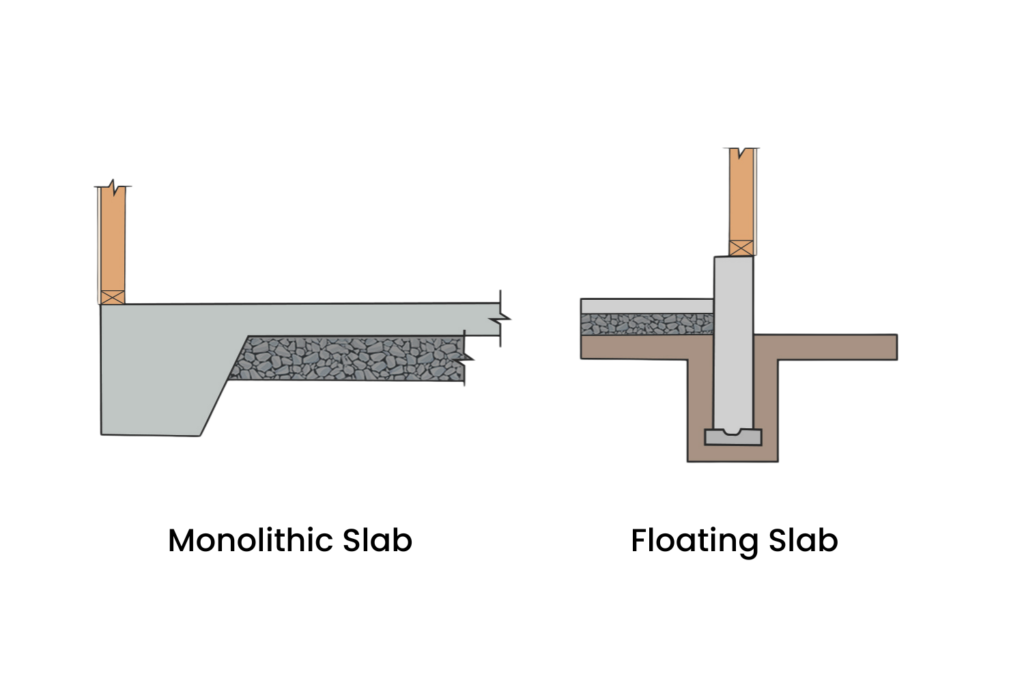
Monolithic Concrete Slab:
This type of slab is typically poured as a single, thick layer of concrete.
It is directly connected or integrated with the footings of the building, forming a single, solid unit.
Monolithic slabs are often used in areas with stable soil conditions and where the water table is not high.
Floating Concrete Slab:
A floating slab is not directly attached to the footings of the building. Instead, it rests on a layer of gravel or sand, allowing it to “float” independently.
Floating slabs are designed to move slightly with the expansion and contraction of the soil beneath them, reducing the risk of cracking.
They are often used in colder climates where frost heave can be a concern, as the floating design helps to minimize the effects of frost on the foundation.
Commonly used for garages, sheds, and small structures where a full foundation may not be necessary or cost-effective.
In summary, the main difference between a monolithic concrete slab and a floating concrete slab lies in their connection to the footings and their suitability for different soil and climate conditions.